
The particulate matter then undergoes compaction and cementation at moderate temperatures and pressures ( diagenesis). This process causes clastic sediments (pieces of rock) or organic particles ( detritus) to settle and accumulate or for minerals to chemically precipitate ( evaporite) from a solution. Sedimentary rocks are formed at the earth's surface by the accumulation and cementation of fragments of earlier rocks, minerals, and organisms or as chemical precipitates and organic growths in water ( sedimentation). Sedimentary sandstone with iron oxide bands Granite and similar rocks, known as granitoids, dominate the continental crust. The oceanic crust is 99% basalt, which is an igneous rock of mafic composition. Only 0.6% are syenite and 0.3% are ultramafic. Of these, 66% are basalt and gabbro, 16% are granite, and 17% granodiorite and diorite. Ībout 65% of the Earth's crust by volume consists of igneous rocks. The content of alkali metal oxides is next in importance. Silica content is thus the most important chemical criterion for classifying igneous rock. This occurs both because minerals low in silica crystallize out of the magma as it begins to cool ( Bowen's reaction series) and because the magma assimilates some of the crustal rock through which it ascends ( country rock), and crustal rock tends to be high in silica. Magmas tend to become richer in silica as they rise towards the Earth's surface, a process called magma differentiation.

Rocks are classified according to characteristics such as mineral and chemical composition, permeability, texture of the constituent particles, and particle size. Rock outcrop along a mountain creek near Orosí, Costa Rica.

Modern technology has allowed the development of new man-made rocks and rock-like substances, such as concrete. Mining developed to extract rocks from the Earth and obtain the minerals within them, including metals. Stone was then used as a major component in the construction of buildings and early infrastructure. This early period, called the Stone Age, saw the development of many stone tools. Humanity has made use of rocks since the earliest humans. Metamorphic rocks are formed when existing rocks are subjected to such high pressures and temperatures that they are transformed without significant melting.

Sedimentary rocks are formed by diagenesis and lithification of sediments, which in turn are formed by the weathering, transport, and deposition of existing rocks.
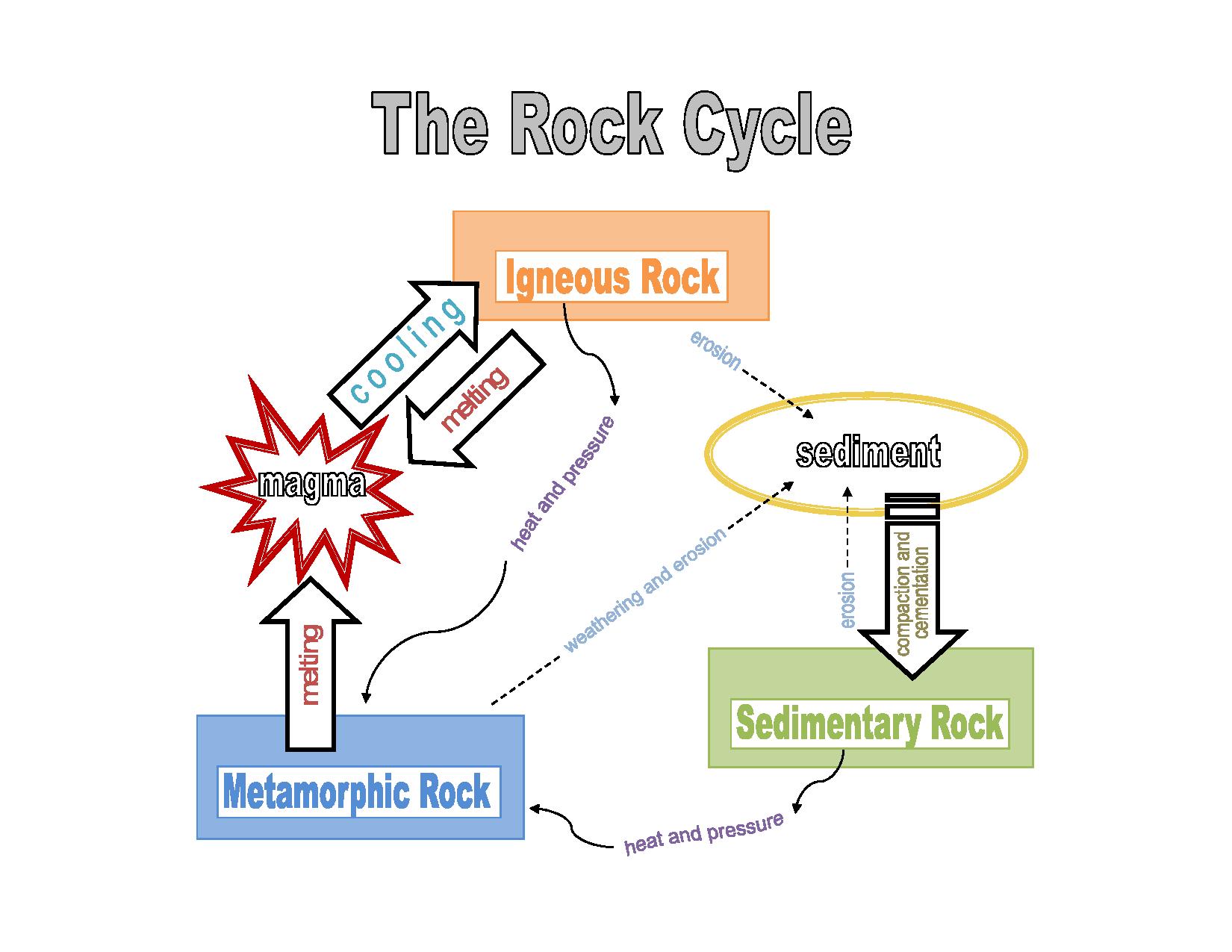
Igneous rocks are formed when magma cools in the Earth's crust, or lava cools on the ground surface or the seabed. Rocks are usually grouped into three main groups: igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks and metamorphic rocks. It may be limited to rocks found on Earth, or it may include planetary geology that studies the rocks of other celestial objects. The study of rocks involves multiple subdisciplines of geology, including petrology and mineralogy. Rocks form the Earth's outer solid layer, the crust, and most of its interior, except for the liquid outer core and pockets of magma in the asthenosphere. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
